Type 1 Diabetes Stem Cell Therapy in India: Advances, Efficacy, and Future Prospects
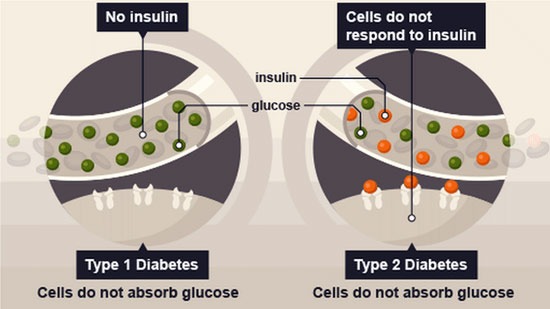
Type 1 Diabetes Stem Cell Therapy India: Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is a chronic condition where the body’s immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Traditional treatments like insulin therapy manage symptoms but don’t cure the underlying cause. However, advancements in stem cell therapy offer promising avenues for treatment.
Understanding Type 1 Diabetes
T1D affects millions globally, typically diagnosed in childhood or adolescence. Patients require lifelong insulin injections to regulate blood sugar levels. Managing T1D involves constant monitoring and balancing insulin doses with diet and exercise.
Role of Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells capable of transforming into specialized cell types. In diabetes, stem cell therapy aims to regenerate pancreatic beta cells destroyed by autoimmune responses. This approach holds potential for restoring insulin production and reducing dependency on external insulin.
Current Research and Clinical Trials in India
India has emerged as a hub for stem cell research and therapy due to advanced medical facilities and skilled professionals. Clinical trials focus on evaluating the safety, efficacy, and long-term benefits of stem cell treatments for T1D. Researchers are exploring various sources of stem cells, including embryonic, induced pluripotent, and adult stem cells, to optimize treatment outcomes.
Benefits and Challenges
Benefits of stem cell therapy for T1D include potential insulin independence, improved blood sugar control, and reduced risk of complications like neuropathy and kidney disease. Challenges include the need for precise cell differentiation, managing immune responses, and ensuring long-term efficacy and safety.
Future Directions and Innovations
Future research aims to refine stem cell protocols, enhance cell survival and integration, and address regulatory hurdles. Innovations like gene editing and biomaterial scaffolds hold promise for enhancing therapeutic outcomes.
Conclusion
Type 1 Diabetes Stem Cell Therapy in India represents a frontier in medical science, offering hope for a cure rather than just management. As research progresses, collaborations between clinicians, researchers, and regulatory bodies will be crucial in translating promising findings into accessible and effective treatments for patients worldwide.